TECHNOLOGY
Designed to be compact, scalable and re-useable
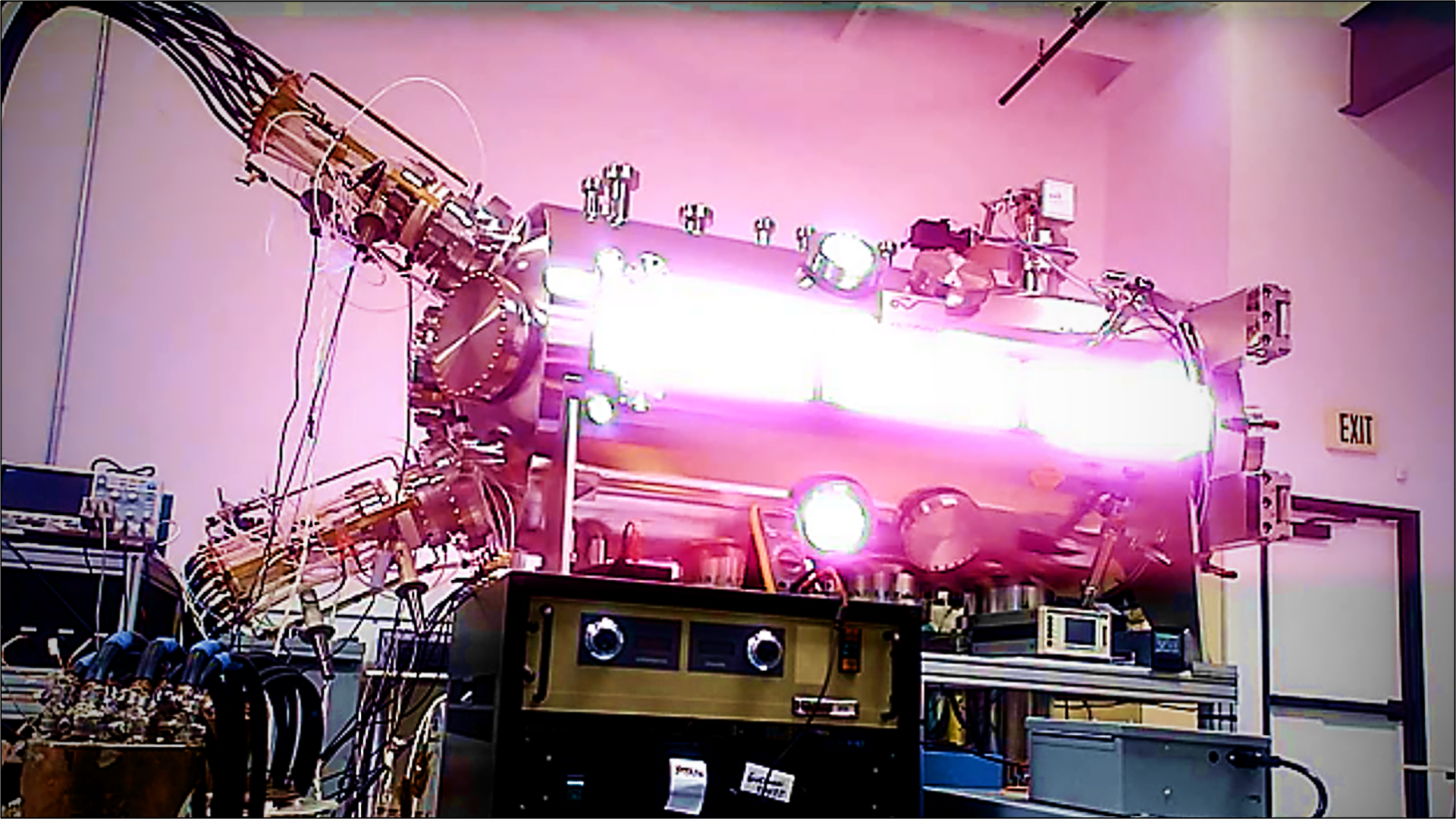
We are advancing a proprietary technology that efficiently converts electricity into plasma heating with a unique, practical scalability in the design to achieve fusion conditions and directly produce thrust.
Compared to other techniques, Helicity focuses on a new magneto-inertial fusion method with self-organized Taylor relaxation and magnetic reconnection physics coupled with a peristaltic magnetic compression scheme. This unique way of confining, heating and compressing plasma is more compact and scalable than conventional magnetic fusion or inertial (laser) fusion.
This brings two major advantages. The first is an extra operational parameter, the number of plasma sources, for scaling the Lawson criterion. The second is the ability to produce thrust at low net gains before self-sustained reactor operation. Therefore, like cylinders in a car engine, our technology can be tested early, scale up with economies of scale, and achieve practical use in space before making electricity (and thrust) as a self-sustained reactor.

“At this point, we need to focus on advances in propulsion technology, rather than spend tens of billions of dollars on a mission that will take years or decades to get there and the same to come back."
- Captain William Readdy, Astronaut and Former NASA Associate Administrator of Space Flight & Helicity Space Advisor
There is no need to wait for terrestrial fusion power to begin using fusion propulsion in space. Pushing a spacecraft with short bursts of fusion can be achieved before (and on the way to) producing net electricity every second. Helicity Drive creates a short burst of fusion conditions in a geometry designed for propulsive plasma exhaust, which provides acceleration with every pulse.
The Helicity Drive is:
-
From cis-lunar to interstellar missions
-
100 kW to GW range
-
No radioactive fuel required
-
Abort, maneuver or fly at anytime
-
Fit for today’s space launch vehicles
-
Little propellant required
What is Fusion Propulsion?
Fusion propulsion is a rocket method that produces thrust from fusion reactions. Fusion reactions happen when two isotopes of hydrogen nuclei merge (fuse) to become a helium nucleus. The main benefit, compared to conventional chemical reactions used in today's rockets, is that fusion produces ten million times more energy per unit mass of fuel. This means less fuel is needed, higher speeds can be achieved, and continuous thrust along agile trajectories are possible.
The team at Helicity is advancing proprietary technology that efficiently converts electricity into plasma heating with a unique, practical scalability in the design to achieve fusion conditions and directly produce thrust. Compared to other techniques, the Helicity Drive is designed from the beginning with the constraints of in-space use in mind. It is built from a unique, pragmatic way of confining, heating and compressing the plasma, resulting in more compact machines than conventional magnetic fusion or inertial (laser) fusion.
Advantages of Fusion Propulsion
Fusion Propulsion
Fuel and Propellant Efficient | Fast for Interplanetary Distances | Less Exposure to Space Radiation | Agile Trajectories (Abort Return Possible) | High Power and High Energy | Mission Opportunities Less Constrained by Orbital Synchronization
- COMPARED TO -
Traditional Propulsion
Consumes a lot of Propellant | Slow for Interplanetary Distances | Long Exposure to Space Radiation | Brief Impulse Then Coast | High-Power but Low Energy | Frequency of Mission Opportunities Severely Constrained by Orbital Synchronization
Scientific Collaborators
Helicity Space has past and ongoing collaborations with pre-eminent scientific institutes around the world including the California Institute of Technology, the Los Alamos National Laboratory, the University of Maryland in Baltimore County, Swarthmore College, the University of Wisconsin, the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS) and the University of Tokyo.
In addition, Helicity Space is proud to be supported in part by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Innovation Network for Fusion Energy (DOE INFUSE) and the Limitless Space Institute’s Interstellar Initiatives (I2), as well as being members of the Fusion Industry Association (FIA), the Commercial Spaceflight Federation (CSF) and the Space Transportation Association (STA).
RESOURCES
For more background on our approach, please visit the resources below.

